Stacks
 A stack
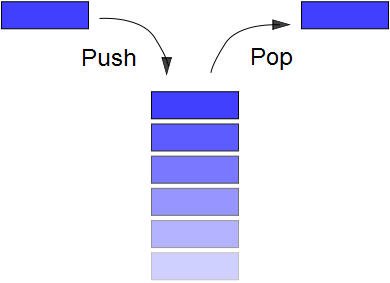
is a last in first out (LIFO) type linear data structure.
A stack
is a last in first out (LIFO) type linear data structure.
 Items
can only be inserted from the top and removed from the top
Items
can only be inserted from the top and removed from the top
 Two of
the more important stack operations involve pushing data onto a stack and
popping data off the stack.
Two of
the more important stack operations involve pushing data onto a stack and
popping data off the stack.
Stack of Books

Push and Pop Operations
Contrasted with the Queue Data Structure

The Stack
 Its
uses span the spectrum from reversing items to depth-first searches in
artificial intelligence applications to keeping track of function calls
Its
uses span the spectrum from reversing items to depth-first searches in
artificial intelligence applications to keeping track of function calls
 It can
be implemented using either a linked list or a one-dimensional array.
It can
be implemented using either a linked list or a one-dimensional array.
 The
following code implements a stack using a linked list
The
following code implements a stack using a linked list
 Note
that it currently only accepts integers. A more useful stack could be created by
using a templated class (remember templated functions?)
Note
that it currently only accepts integers. A more useful stack could be created by
using a templated class (remember templated functions?)
//This program implements a stack using a linked list
#include
"stdafx.h"
#include<iostream>
using
namespace
std;
struct
node
{
int
data;
struct node *next;
};
class
stack
{
private:
struct node *top;
public:
stack()
// constructor
{
top=NULL;
}
void push(); // to
insert an element
void pop();
// to delete an element
void show(); // to
show the stack
};
// PUSH
Operation
void
stack::push()
{
int
value;
struct node *ptr;
cout<<"\nPUSH
Operation\n";
cout<<"Enter
a number to insert: ";
cin>>value;
ptr=new
node;
ptr->data=value;
ptr->next=NULL;
if(top!=NULL)
ptr->next=top;
top=ptr;
cout<<"\nNew
item is inserted to the stack.";
}
// POP Operation
void
stack::pop()
{
struct node *temp;
if(top==NULL)
{
cout<<"\nThe
stack is empty!";
return;
}
temp=top;
top=top->next;
cout<<"\nPOP
Operation........\nPoped value is "<<temp->data;
delete temp;
}
// Show stack
void
stack::show()
{
struct node *ptr1=top;
cout<<"\nThe
stack is: ";
while(ptr1!=NULL)
{
cout<<ptr1->data<<" ->";
ptr1=ptr1->next;
}
cout<<"NULL\n";
}
// Main function
int
main()
{
stack s;
int
choice;
while(1)
{
cout<<"\n-----------------------------------------------------------";
cout<<"\n\t\tSTACK
USING LINKED LIST\n\n";
cout<<"1:PUSH,
2:POP, 3:DISPLAY STACK, 4:EXIT";
cout<<"\nEnter
your choice(1-4): ";
cin>>choice;
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
s.push();
break;
case 2:
s.pop();
break;
case 3:
s.show();
break;
case 4:
exit(0);
break;
default:
cout<<"Please enter correct choice(1-4)!";
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
